Organisation and personnel
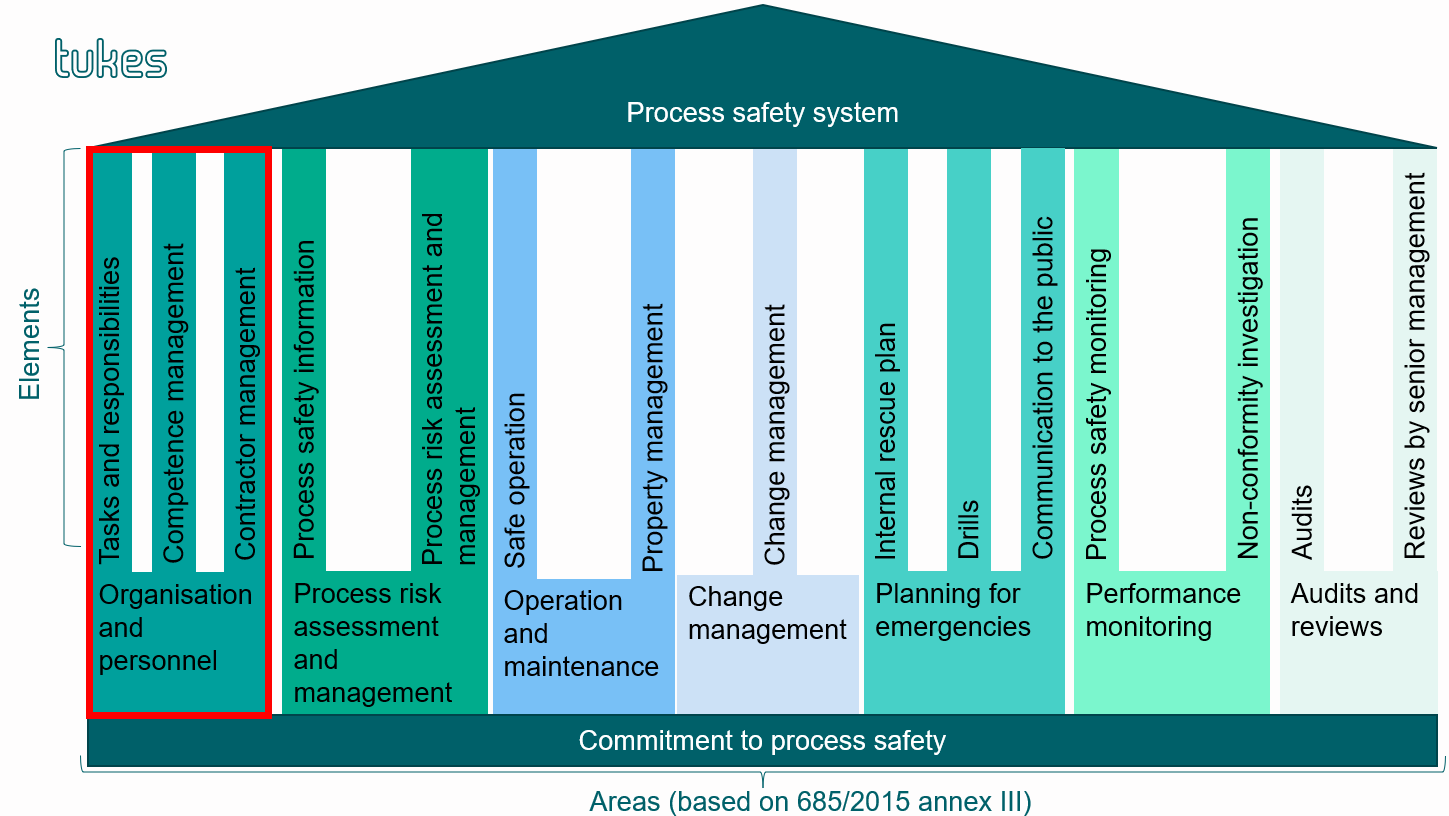
’Organisation and personnel’ is an area of the process safety system consisting of three elements: tasks and responsibilities; competence management; and contractor management.
The goal of the area is to identify persons responsible for process safety management and define tasks and competence requirements for process safety management at different organisational levels.
Persons responsible for process safety include the chemicals and LPG supervisor as well as the person responsible for operating principles. The personnel’s job-specific needs for process safety competence and training must be defined. Training must be planned and documented.
Contractors also play a key role in process safety management. Induction must be provided for contractors regarding the worksite and risks surrounding it, and it must be ensured that contractors have sufficient competence and knowledge regarding process safety procedures.
TASKS AND RESPONSIBILITIES
Requirement
At their production plant, economic operators must appoint a chemicals and/or LPG supervisor who has passed the qualification examination of Tukes.
Approved procedure
The operations supervisor’s qualification examination is completed in eTentti service (in Finnish).
The matters defined under the operations supervisor’s rights and obligations are taken into account in the appointment.
The Tukes course in the eTentti service (in Finnish) prepares operations supervisors for the qualification examination.
A certificate of the operations supervisor’s qualification examination has been entered in the Tukes examination system and/or is held by the supervisor.
The qualification examination must be taken again if it was completed before 2013. However, a person can continue as an operations supervisor if they were appointed before 1 January 2013.
As a rule, the role of an operations supervisor cannot be outsourced as the supervisor must be a member of the production plant’s personnel.
An LPG supervisor must always be appointed when there is more than 5 t of LPG at the production plant.
Requirement
The operations supervisor’s rights, responsibilities and obligations, as well as the hours available for the role, must be defined in writing, and the supervisor must give their consent to the role.
Approved procedure
The operations supervisor’s tasks and responsibilities, as well as any limitations on their role, are entered in the supervisor’s appointment document or job description.
A single production facility may have several operations supervisors whose responsibilities are distributed (e.g. by production line or department). In these cases, the limitations on the role must be described.
Requirement
Economic operators must ensure that the operations supervisor’s tasks are carried out in situations where the supervisor is absent. When the operations supervisor is replaced, the economic operator must appoint a new supervisor within three months.
Approved procedure
An economic operator appoints a deputy operations supervisor who has completed the qualification examination of Tukes and to whom the primary supervisor’s tasks are transferred in the case of absence.
The deputy operations supervisor must be appointed similarly to the primary supervisor.
Requirement
Economic operators must ensure that, to properly carry out their tasks, the operations supervisor has a sufficient know-how regarding the processes for which they are responsible.
Approved procedure
The operations supervisor is provided with documented induction regarding the plant’s risks, technical implementation and safety management system.
Requirement
Economic operators must identify and appoint other statutory key employees required for their operations.
Approved procedure
Appointed key employees include a natural gas supervisor, pressure equipment supervisor, boiler plant supervisor and an operation manager of an electrical installation. The aforementioned key employees must be named in accordance with the instructions presented on the Tukes website:
Pressure equipment supervisor (in Finnish)
Operation manager of an electrical installation
Requirement
Economic operators must appoint a person responsible for each area of the process safety system.
Approved procedure
Either a single responsible person can be appointed (for operating principles), or responsibilities can be divided between several persons.
Economic operators must ensure that a responsible person or persons is/are appointed.
Requirement
Economic operators must assess the need for a person responsible for the safety automation system and appoint the person or persons.
Approved procedure
A person or persons responsible for the safety automation system must be appointed if the production plant has a safety automation system. The appointment is also required in the IEC 61511 standard.
The tasks and responsibilities of the person responsible for the safety automation system are presented in the standard. Economic operators can define their appointment practices.
The person responsible for the safety automation system is a key role in terms of process safety, and any changes in the role must be handled similarly to changes in other statutory roles of responsibility.
Requirement
Economic operators must define task-specific responsibilities for process safety in writing and provide the responsible person with a sufficient number of working hours to fulfil their responsibilities.
Approved procedure
Responsibilities and the hours available to fulfil them must be documented: in a job description, rescue plan, major accident prevention policy document or safety report.
Requirement
Economic operators must communicate process safety responsibilities and responsible persons to the personnel.
Approved procedure
Communication methods depend on the size of the organisation. A table of process safety responsibilities may be included in the induction programme or it may be displayed on a notice board or the company’s intranet.
Requirement
Economic operators must have documented procedures in place to identify any amendments to chemical safety legislation and assess the impact of the amendments.
Approved procedure
The economic operator’s representatives have subscribed to the Tukes newsletter for process safety.
The economic operator follows the Tukes Edilex service for any legal amendments.
Legal amendments concerning the production plant are documented, and the measures required by them are monitored.
COMPETENCE MANAGEMENT
Requirement
Economic operators must assess and define the personnel’s task-specific process safety competence and training needs.
Approved procedure
Task-specific competence and training needs regarding process safety must be defined in writing.
As a result of an assessment, not all tasks may necessarily require the definition of process safety competence and training needs.
Requirement
Economic operators must provide their personnel with process safety training. Training must be repeated regularly if required.
Approved procedure
Process safety training is included in the training plan.
The training theme must be identified if possible, e.g. ATEX, process safety training, CLP labelling training, training after significant changes in the preparation of an explosion protection document or other significant changes.
The risk analyses conducted must be addressed in training. A good practice in more complicated processes is to use bowtie methods in training.
Requirement
Economic operators must maintain records of training provided as well as the personnel’s competence and qualifications.
Approved procedure
All training must be registered. The training register must provide an overview of training provided for each employee. This means that training information about each training event held (list of participants) and each employee (list of completed training, possible qualifications, etc.) must be recorded.
Requirement
New employees must be provided with induction regarding the plant’s process safety hazards. Induction must also be provided in conjunction with changes in tasks.
Approved procedure
An economic operator has an induction programme and material for new employees, including the plant’s process safety hazards and preparations for them. The completion of induction must be recorded and signed.
CONTRACTOR MANAGEMENT
Requirement
Economic operators must address safety, competence and qualifications in competitive bidding for contractors.
Approved procedure
Each contractor’s abilities and qualifications regarding process safety are addressed in the procurement notice, for example.
Requirement
Economic operators must have a procedure in place to ensure that statutory qualification requirements set for contractors are met.
Approved procedure
An economic operator has procurement instructions or a procurement checklist.
Statutory qualifications include the supervisor of electrical work. In addition, the hot work and occupational safety cards are recommended.
Requirement
Economic operators must define the work to be carried out and the competence requirements set for it, and when selecting a contractor, ensure that the contractor has a sufficient competence in the task at hand.
Approved procedure
The verification of competence and qualifications are addressed in procurement instructions.
Requirement
Economic operators must define contact people between the contractor and economic operator, as well as practices for information exchange, throughout the duration of the worksite.
Approved procedure
Contact people and information exchange practices can be defined in the procurement agreement, work permit, project meeting memoranda or another written document.
Requirement
Contractors must be provided with plant-specific induction.
Approved procedure
An economic operator has a plant induction programme and material, and records of induction are maintained. The programme includes general safety information applied to everyone, including alarms, assembly points, and the safety equipment required.
Requirement
Contractors must be provided with task-specific induction, including the chemicals and processes related to the task as well as the definition of the work area in the field.
Approved procedure
Records of the induction provided are maintained. Induction can be acknowledged in the work permit, for example.
Requirement
Contractors must be provided with sufficient training regarding the internal rescue plan.
Approved procedure
Training regarding the internal rescue plan can be provided as separate safety induction or in conjunction with the work permit.
Requirement
Economic operators must have a procedure in place to coordinate the tasks of its employees and various subcontractors.
Approved procedure
When issuing a work permit, it is ensured that other work carried out in the area has been addressed in it. An electronic system can also be used.
Requirement
Economic operators must be aware and maintain records of the number of their employees, visitors and employees of subcontractors in the area.
Approved procedure
Records are maintained at the production plant, allowing it to be immediately verified who is present (e.g. in the event of an accident).