Electric personal transportation devices
The legislation and requirements applied to electric personal transportation devices depend on the features of each device. The product itself may be covered by machine regulation and/or vehicle regulation. The use of electric personal transportation devices, on the other hand, is regulated by road traffic legislation.
All other electric personal transportation devices, except those covered by EU Regulation 168/2013 (e.g. electric scooters with a maximum speed of more than 25 km/h approved for road use), are covered by machine regulation.
The Vehicles Act defines several vehicle categories, such as light electric vehicles and electrically assisted bicycles. Devices to assist walking are not covered by the Vehicles Act. The vehicle categories may have implications for road use.
The distinction between different categories is usually based on the device's maximum speed and power.
| Legislation and requirements | Devices to assist/replace walking | Light electric vehicles | Electrically assisted bicycles | Motorised bicycles (L1e-A) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Examples |
|
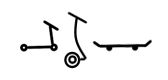
|
|

|
| Market surveillance authority | Tukes | Traficom | Traficom | Traficom |
| Primary legislation | Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Machinery Decree 400/2008 |
Vehicles Act 1090/2002 Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Machinery Decree 400/2008 |
Vehicles Act 1090/2002 Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Machinery Decree 400/2008 |
Vehicles Act 1090/2002 |
| Maximum speed and power | 15 km/h and 1 kW | 16-25 km/h and 1 kW | 25 km/h and 250 W | 25 km/h and 1 kW |
More information
Tukes:
Electromagnetic compatibility - EMC
Hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment – RoHS
Traficom: transport and communication services for you
Police: Traffic safety and surveillance